Description
In Depth
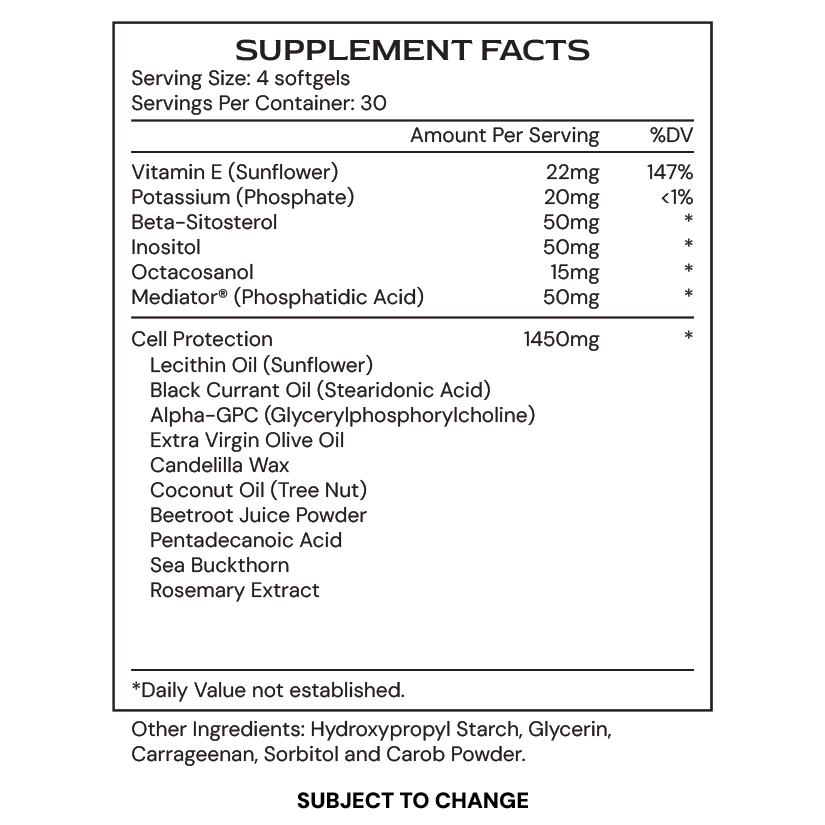
CellGenic by Alimentum Labs is a cutting-edge supplement designed to support cellular membrane integrity, enhance regeneration, and promote heart and brain health. This powerful blend of phospholipids, lipid antioxidants, and essential fatty acids—including pentadecanoic acid—improves membrane fluidity, protects against cellular leakage, and boosts energy production. The components of this formula activate key genes like the PPAR gene family, supporting the body’s natural anti-aging processes, detoxification, and hormone balance. With its combination of antioxidants, botanicals, and amino acids, CellGenic optimizes cellular function, promotes cardiovascular and cognitive health, and offers comprehensive support for longevity and vitality.
Key Features
- Sea buckthorn supports cellular integrity and membrane health through its rich content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, flavonoids, and antioxidants, which enhance lipid metabolism and reduce oxidative stress. It regulates key genes involved in mitochondrial function, insulin sensitivity, and antioxidant defense, such as PPARs, GLUT4, NFE2L2, and PGC-1α, promoting cellular resilience and benefiting both metabolic and cognitive health.
- Vitamin E, particularly α-tocopherol, supports cell membrane stability by acting as a potent antioxidant, preventing lipid peroxidation and enhancing membrane fluidity. It also regulates key cellular pathways involved in inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular health, while promoting vascular protection and energy production, which benefit overall cardiovascular and cognitive function.
- Octacosanol supports cellular function by activating AMPK and PPAR, which enhance lipid metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate cholesterol production by downregulating HMG-CoA reductase. It also helps maintain membrane integrity by reducing inflammatory markers such as VCAM-1 and PE-Selectin in endothelial cells, supporting healthy lipid profiles and improving vascular function.
- Beta-sitosterol, a plant-derived phytosterol, integrates into cellular and mitochondrial membranes, enhancing their fluidity and stability while supporting vital signaling processes. It helps regulate genes involved in cell survival and inflammation, while also improving mitochondrial function and resistance to oxidative stress, ultimately contributing to cellular health and protecting against damage.
- Inositol is an essential nutrient that supports membrane stability by being a key component of phosphatidylinositol and phosphoinositides, which are crucial for cell signaling and trafficking. It regulates important metabolic pathways like the PI3K/Akt pathway, promoting cell survival and glucose metabolism, while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Additionally, inositol helps protect against cellular stress and neurodegeneration, contributing to overall cellular health and supporting both metabolic and cognitive function.
White Paper
The White Paper is your comprehensive guide to understanding this product. It details the ingredients, their functions, and how they work together to deliver results. Complete with usage guidance and safety information, it’s an invaluable resource for anyone seeking a thorough understanding of this formula.
Essential Ingredients
- Sea Buckthorn
- Vitamin E
- Octacosanol
- Beta-sitosterol
- Inositol
Directions
Take 4 capsules daily, or as directed by your health care provider.
Warnings
Keep away from heat, sunlight, and out of the reach of children.
Quality Guarantee
cGMP facility
Vegan
Non-GMO
Gluten Free
Dairy Free
No Sugar
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should take CellGenic?
CellGenic is ideal for anyone looking to support cellular health, boost energy, promote heart and brain health, and enhance detoxification and hormonal balance. It’s especially beneficial for those seeking anti-aging benefits, optimal cellular function, and scientifically-backed wellness support.
How should I take CellGenic?
Take 4 capsules of CellGenic daily, or as directed by your health care provider, for optimal results.
Can I take CellGenic with other supplements?
Yes, you can take CellGenic with other supplements. However, it’s always a good idea to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure compatibility with any other products you’re using, and to determine if it can be safely combined with any medications.
Can I take CellGenic if I'm pregnant?
Yes, you can take CellGenic during pregnancy, as it contains ingredients that are essential for a healthy pregnancy. However, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before adding any new supplement to your routine while pregnant to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual needs.
Why is phosphatidic acid important for support the fluidity of cellular membranes?
Phosphatidic acid is important for supporting the fluidity of cellular membranes because it plays a crucial role in maintaining membrane structure and function. As a key component of phospholipids, which make up the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, phosphatidic acid helps to regulate membrane flexibility. This fluidity is essential for proper cellular communication, nutrient and oxygen transport, and efficient waste removal. By supporting membrane fluidity, phosphatidic acid ensures that the cells can adapt to changes in their environment, improve nutrient absorption, and enhance overall cellular function.
How does CellGenic support membrane integrity?
CellGenic supports membrane integrity through its unique blend of phospholipids, lipid antioxidants, and essential fatty acids like pentadecanoic acid. These ingredients work together to improve membrane fluidity, protect against cellular leakage, and support the overall structure and function of cellular membranes. This nourishment helps maintain healthy, resilient cell membranes, which are critical for optimal cellular health and performance.











There are no reviews yet.