Description
In Depth
HormoneGenic by Alimentum Labs delivers a powerful blend of phytonutrients and clinically validated herbs to support optimal hormone balance and metabolism. Designed to harmonize your endocrine system, this advanced formula targets key sex hormones—estrogens, progestogens, and androgens—to enhance reproductive health, manage symptoms of menopause, and address hormonal imbalances. Suitable for both women and men, HormoneGenic supports overall well-being and mitigates the effects of hormonal fluctuations, helping you achieve a more balanced and revitalized state through every phase of life.
Key Features
- Rheum rhaponticum, specifically its extract ERr 731, supports hormone balance by interacting with estrogen receptors, which helps alleviate menopause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and irritability. By modulating estrogen receptor activity, it aids in stabilizing hormonal fluctuations, thereby supporting overall endocrine function and improving quality of life during hormonal transitions.
- Indole-3-carbinol (I3C) supports hormone balance by promoting the conversion of estrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, a form of estrogen that has protective effects against estrogen-dependent cancers. Additionally, I3C helps regulate estrogen metabolism and downregulates genes activated by estrogen receptors, thereby contributing to a healthier hormone profile and improved metabolic function.
- Diindolylmethane (DIM) supports healthy hormone function by helping to balance estrogen levels and enhance the body’s response to hormone-related changes. Its potent effects, including the potential to inhibit cellular growth and protect against estrogen-dependent cancers, contribute to overall hormonal balance and metabolic health.
- Vitex agnus-castus, or chasteberry, is effective in alleviating symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), including mood swings, fatigue, and breast pain. Its benefits are attributed to its ability to regulate dopamine and opioid receptors, as well as inhibit excessive prolactin release from the pituitary gland.
- Angelica sinensis, or female ginseng, supports bone health and prevents osteoporosis similarly to estrogen replacement therapy by modulating genes like PPARγ and iNOS. It also promotes red blood cell production, benefits heavy menstrual bleeding, and may help manage PCOS symptoms by regulating CYP17A1 and CYP19A1 genes.
White Paper
The White Paper is your comprehensive guide to understanding this product. It details the ingredients, their functions, and how they work together to deliver results. Complete with usage guidance and safety information, it’s an invaluable resource for anyone seeking a thorough understanding of this formula.
Essential Ingredients
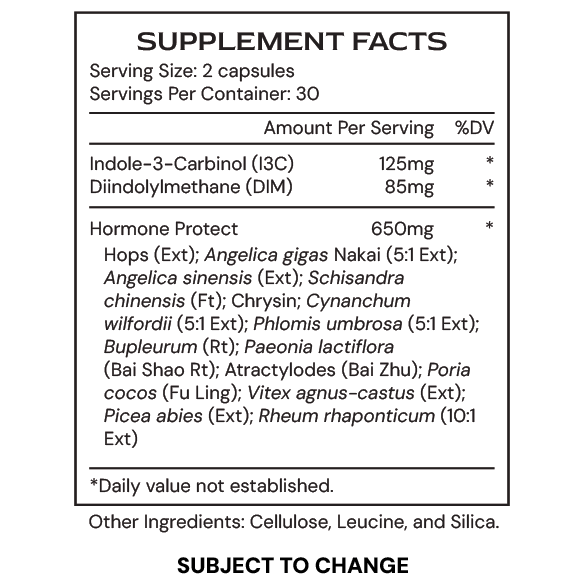
- Rheum rhaponticum
- Indole-3-carbinol
- Diindolylmethane (DIM)
- Vitex agnus-castus
- Angelica sinensis
Directions
Take 2 capsules daily with food, or as directed by your health care provider.
Warnings
Not recommended for use during pregnancy, while nursing, or while taking fertility medications.
Quality Guarantee
cGMP facility
Vegan
Non-GMO
Gluten Free
Dairy Free
No Sugar
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should take HormoneGenic?
HormoneGenic is suitable for individuals seeking to balance their hormones, including those experiencing symptoms of hormonal imbalances, such as mood swings, fatigue, or irregular menstrual cycles. It is also beneficial for those undergoing hormonal transitions like menopause or dealing with hormone-related conditions such as PCOS or infertility.
How should I take HormoneGenic?
Take 2 capsules of HormoneGenic daily with food, or follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Can I take HormoneGenic with other supplements?
Yes, you can take HormoneGenic with other supplements, such as Hormone μBiomic and Hormone Superfood, for enhanced hormone support. However, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your daily routine.
Can I take HormoneGenic if I'm pregnant?
HormoneGenic is generally safe for use, but it is not recommended during pregnancy, while nursing, or when taking fertility medications. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement under these conditions.
Why is Diindolylmethane (DIM) important for hormone metabolism?
Diindolylmethane (DIM) is important for hormone metabolism because it helps regulate estrogen levels and promotes a healthy balance of estrogen metabolites. This regulation can support overall hormonal balance and reduce the risk of estrogen-dependent issues, including certain cancers.
How does HormoneGenic improve energy and mood?
HormoneGenic improves energy and mood by balancing hormone levels, which can help alleviate symptoms like fatigue and mood swings. Its blend of ingredients supports hormonal regulation, which in turn enhances overall well-being and energy levels.
Can men take HormoneGenic?
Yes, men can take HormoneGenic. It supports hormonal balance and addresses issues such as low energy, mood swings, and hormonal imbalances that can affect both men and women.










There are no reviews yet.