Description
In Depth
Elevate your cognitive capabilities to new heights with NeuroGenic, a revolutionary nootropic supplement meticulously formulated to unleash the full potential of your mind. Designed to protect and enhance cognitive functions by modulating the expression of key genes like APOE, BDNF, and DRD2, NeuroGenic offers a revolutionary approach to cognitive enhancement.
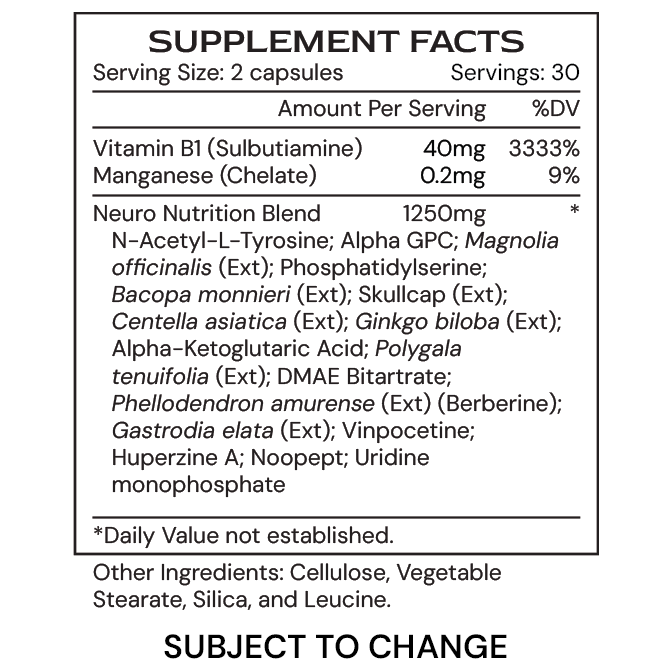
Crafted with precision and backed by scientific research, this cutting-edge nootropic supplement enhances your cognitive capabilities to unlock the boundless potential of your mind. With a powerful blend of scientifically-backed ingredients, including Centella asiatica, Polygala tenuifolia, Alpha-GPC, Noopept and Magnolia officinalis, NeuroGenic promotes neuroplasticity, memory recall, and mood elevation, ensuring peak cognitive performance.
From synergistic brain support to neuroprotective power, each element of NeuroGenic is meticulously formulated to safeguard your brain cells, optimize energy levels, and enhance overall cognitive function. Embrace the next level of cognitive empowerment and unlock a sharper mind, improved mood, and sustained focus with NeuroGenic today!
Key Features
- Centella asiatica, also known as Gotu Kola, supports and enhances cognitive function by improving brain health through its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. It promotes neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and memory by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and amyloid-β buildup. Additionally, its active compounds support mitochondrial function, regulate key brain pathways, and help maintain brain energy balance, making it a valuable herb for improving focus, mood, and overall brain performance.
- Polygala tenuifolia, also known as Yuan Zhi, supports cognitive health through its triterpene saponins, including onjisaponins, which increase Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) expression, enhancing learning, memory, and overall brain function. It also boosts Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) production, promoting neuron growth, survival, and maintenance. Additionally, Polygala tenuifolia helps regulate the nervous system by increasing GABA levels and reducing dopamine and DRD2 expression, offering a calming effect that can aid in memory dysfunction, insomnia, and anxiety.
- Alpha-GPC (Glyceryl Phosphoryl Choline) enhances cognitive function by increasing acetylcholine levels, which are essential for memory, learning, and neuroplasticity. It promotes neuronal growth and repair, protects against oxidative stress, and may help slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, Alpha-GPC improves memory retention, focus, and mental clarity by boosting brain metabolism and increasing blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain.
- DMAE Bitartrate supports cognitive health by enhancing acetylcholine synthesis, crucial for memory, attention, and brain function. It increases choline levels in the brain, aiding cognitive processes and potentially treating mild cognitive impairment. DMAE also regulates neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which influence mood and focus, and modulates adrenergic responses, helping with age-related cognitive decline.
- Magnolia officinalis, rich in bioactive compounds like magnolol and honokiol, works to improve cognitive function by reducing neuroinflammation and protecting neurons from damage. Research suggests that magnolol can help address cognitive deficits, while honokiol promotes myelin repair and reduces cognitive decline. Additionally, magnolia officinalis has shown potential in disrupting beta-amyloid plaques, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and may aid in recovery from white matter injury.
White Paper
The White Paper is your comprehensive guide to understanding this product. It details the ingredients, their functions, and how they work together to deliver results. Complete with usage guidance and safety information, it’s an invaluable resource for anyone seeking a thorough understanding of this formula.
Essential Ingredients
- Centella asiatica
- Polygala tenuifolia
- Alpha-GPC
- DMAE Bitartrate
- Magnolia officinalis
Directions
Take 2 capsules daily, or as directed by your health care provider.
Warnings
Keep away from heat, sunlight, and out of the reach of children.
If taking blood thinners, anti-hypertensives, sedatives, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, or dopamine-modulating drugs, consult a healthcare professional before taking NeuroGenic.
Quality Guarantee
cGMP facility
Vegan
Non-GMO
Gluten Free
Dairy Free
No Sugar
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should take NeuroGenic?
NeuroGenic is ideal for individuals seeking to enhance their cognitive capabilities, improve memory recall, sharpen focus, elevate mood, and amplify overall cognitive performance. It’s particularly beneficial for students, professionals, athletes, and anyone looking to optimize their mental clarity and performance during demanding tasks. Additionally, individuals experiencing cognitive decline associated with aging or seeking long-term brain health support can also benefit from NeuroGenic’s neuroprotective properties and holistic brain support.
How should I take NeuroGenic?
To reap the full benefits of NeuroGenic, take 2 capsules daily with a meal or as directed by your health care practitioner. Consistency is key to experiencing optimal results, so incorporate NeuroGenic into your daily routine to support your cognitive health and performance effectively. Remember to follow the recommended dosage and consult with your health care provider if you have any specific health concerns or conditions.
Can I take NeuroGenic with other supplements?
Yes, you can definitely take NeuroGenic alongside other supplements, particularly those from Alimentum Labs that are designed to support brain health. Combining NeuroGenic with other brain-boosting supplements can provide comprehensive support for cognitive function and overall brain health. However, it’s always a good idea to consult with your health care provider before adding new supplements to your regimen to ensure they complement each other well and are suitable for your individual needs.
Can I take NeuroGenic if I'm pregnant?
Yes, NeuroGenic is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when taken as directed. However, it is always recommended to consult with your health care provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially during pregnancy, to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific situation and to address any potential concerns or interactions. Your health care provider can provide personalized guidance based on yours and your baby’s individual health needs and circumstances.
Why is Alpha-GPC important for inhibiting cognitive decline?
Alpha-GPC, a derivative of choline, is vital for maintaining the integrity of brain cell membranes by providing both structural and function support. These protective properties help safeguard neurons from damage and deterioration, thus preserving cognitive function and overall brain health. Additionally, Alpha-GPC facilitates the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for memory and learning, further contributing to its neuroprotective effects.
How does NeuroGenic heighten focus and concentration?
NeuroGenic heightens focus and concentration through a unique combination of ingredients that promote optimal brain function. These components work together to improve blood flow to the brain and enhance neurotransmitter function, resulting in sustained mental clarity and focus during demanding tasks.













There are no reviews yet.